Different USB Types, USB Ports, and USB Connectors Guide
USB technology is used in a variety of electronic devices, from smartphones and tablets to complex computer systems and peripherals. This guide details the various USB types, ports, and connectors to help you understand their differences, compatibility, and uses.
Understanding USB Standards
The USB standard has evolved since its inception, with each evolution bringing improvements in speed, power transfer, and functionality.
USB 1.1: Launched in 1998, this early version supports speeds up to 12 Mbps and is mostly obsolete today.
USB 2.0: Introduced in 2000, it significantly increased the speed to 480 Mbps and added more power output capabilities. It’s still widely used for peripherals that don’t require high data transfer rates.
USB 3.0: Debuted in 2008, USB 3.0 marked a substantial improvement, offering speeds up to 5 Gbps and better power efficiency. It’s backward compatible with USB 2.0 devices and ports.
USB 3.1: Released in 2013, this version increased data transfer rates to 10 Gbps and improved power delivery to support more robust devices.
USB4: The latest standard, introduced in 2019, USB4 can reach speeds up to 40 Gbps and supports multiple simultaneous data and display protocols.
Each new version of USB is made to keep up with the needs of today’s gadgets. They make data move faster and give power to devices more reliably, like phones, computers, and other tech stuff.
Types of USB Connectors and Ports
USB connectors and ports are integral components of device connectivity, each serving a unique function yet closely interrelated.
USB Connectors

These are the ends of cables that plug into devices. The most familiar types include:
- USB-A: Recognizable by its flat, rectangular shape, used mainly to connect devices to hosts like computers and chargers.
- USB-B: Square-shaped with beveled corners, found on cables that link larger devices such as printers to computers.
- Mini-USB: Previously common in older mobile devices, now largely replaced by Micro-USB and USB-C.
- Micro-USB: Compact and durable, widely used in smartphones and small electronics.
- USB-C: The latest and most adaptable, featuring a reversible design that supports high-speed data, video, and power delivery.
USB Ports
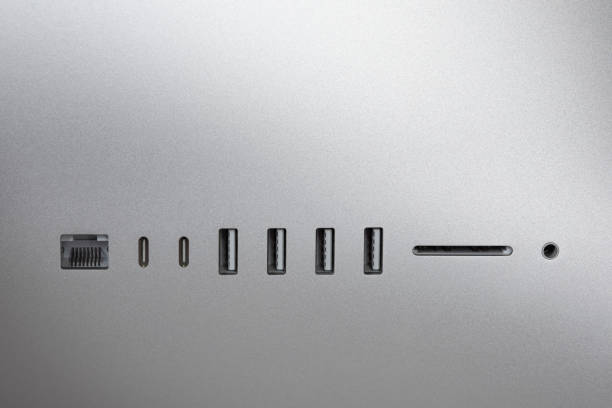
These are the interfaces on devices where the connectors are inserted. Common types include:
- USB-A Port: The standard port is seen on computers and chargers, matching the USB-A connector’s flat, rectangular design.
- USB-B Port: Less common, found on larger peripherals requiring a computer connection and designed to prevent incorrect insertion.
- Mini-USB and Micro-USB Ports: While Mini-USB ports are now rare, Micro-USB ports are still prevalent in many devices, suited to the smaller size of the Micro-USB connector.
- USB-C Port: Supports cutting-edge USB standards such as USB 3.1 and USB4, found on newer devices, and facilitates easy, orientation-free connections.
- Specialized USB Ports: Such as USB 3.0 ports marked by blue color coding, indicate higher transfer speeds compared to the older USB 2.0 standards in black or white ports.
By understanding the specific types and functions of USB connectors and ports, users can ensure compatibility between cables and devices, optimizing their use for efficient data transfer and charging.
USB Cables and Their Uses
Each type of USB cable is designed for specific functions and compatibility with different USB standards and connector types. Here’s an overview of various USB cables and their primary uses:
- USB-A to USB-B Cables
Commonly used to connect large peripherals such as printers, scanners, and external hard drives to computers. The USB-A end plugs into the computer, while the USB-B end fits into the device.
- USB-A to Mini-USB Cables
Previously popular for connecting older mobile devices and digital cameras. These cables are less common now but are still used for some devices requiring a Mini-USB connection.
- USB-A to Micro-USB Cables
Widely used for charging and data transfer with many smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. This cable type remains popular due to the vast number of devices that still rely on Micro-USB ports.
- USB-A to USB-C Cables
These cables are increasingly used as more devices adopt USB-C ports. They support fast data transfer and charging speeds and can connect USB-C devices to USB-A ports commonly found on older computers and chargers.
- USB-C to USB-C Cables
These cables are capable of carrying data, video, and power simultaneously, supporting the latest USB 3.1 and USB4 standards. Ideal for connecting modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets to each other or to USB-C chargers and accessories.
- SpecializedUSB Cables
There are also specialized cables like USB 3.0 cables, which are distinguishable by their blue tips and are used for devices that require higher data transfer rates. These are perfect for devices like external SSDs and high-definition cameras that benefit from USB 3.0’s enhanced capabilities.
Understanding the types of USB cables and their specific uses can help in choosing the right cable for your device. This knowledge is important for both the casual user who uses the device on a daily basis and the technical professional.
Advancements in USB Technology
USB technology has undergone significant advancements since its introduction, with key developments including USB 3.0 and 3.1, which greatly increased data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps. The introduction of USB Power Delivery allows for up to 100 watts of power, facilitating the charging of larger devices like laptops via USB. The USB-C connector, notable for its small, reversible design, supports USB PD and alternate modes such as DisplayPort, enhancing versatility.
The latest USB4 standard integrates Thunderbolt 3 technology, doubling speeds up to 40 Gbps and allowing for simultaneous data and display transfers. These improvements have not only streamlined power and data connectivity across a wide range of devices but also set a universal standard that promises increased compatibility and efficiency moving forward.
Practical Tips for Using USB Devices
Using USB devices efficiently and safely requires some practical knowledge to avoid common issues and extend the life of your devices. Here are some essential tips:
- Use the Correct Cable for Your Device
Always ensure that the cable you are using matches the USB standard of your device for optimal performance. Using a USB 2.0 cable with a USB 3.0 device, for instance, will limit the device’s performance capabilities.
- Properly Connect and Disconnect Devices
Always safely eject a USB device from your computer before physically unplugging it. This helps prevent data loss and corruption, especially with storage devices like USB flash drives and external hard drives.
- Keep Ports and Connectors Clean
Dust and debris can accumulate in USB ports and on connectors, potentially causing poor connections and device malfunctions. Use compressed air or a soft brush to keep ports clean.
- Avoid Using Too Many Devices at Once
Overloading USB ports with too many devices can lead to power distribution issues, especially if the devices are high-power. Use a powered USB hub to manage multiple connections efficiently.
- Inspect Cables and Ports Regularly
Check for signs of wear or damage to cables and ports. Frayed cables or bent connectors should be replaced to prevent damage to connected devices.
- Update Your System Drivers
Ensure that your computer’s USB drivers are up to date. Updated drivers can fix bugs, improve performance, and increase compatibility with connected USB devices.
Following these practical tips will help you maintain the functionality and longevity of your USB devices and ensure stable and reliable performance.
Conclusion
Simply put, the evolution of USB technology and its components, including various types of connectors and ports, has enhanced the connectivity and functionality of a wide range of electronic devices. From the outdated Mini-USB to the modern, reversible USB-C, each connector and port has a specific purpose to ensure the efficient operation of your device. Understanding these differences will help you better utilize your device.
For the best printing results, using the right accessories is just as important as choosing a high-quality printer. At YB Toner, we offer quality ink and toner cartridges, focusing on delivering superior Brother Toner and Brother Ink products to ensure your printer is running at its best. Whether you need a reliable USB cable to connect your Brother printer or refill ink and toner supplies, we’ve got you covered. Explore our comprehensive range of printer supplies, including Brother toner and Brother ink, and enhance your printing experience with guaranteed quality and reliability. Visit us today and find all your necessary printing accessories in one place.
Related reading: What is the Difference between USB and HDMI Cables?

